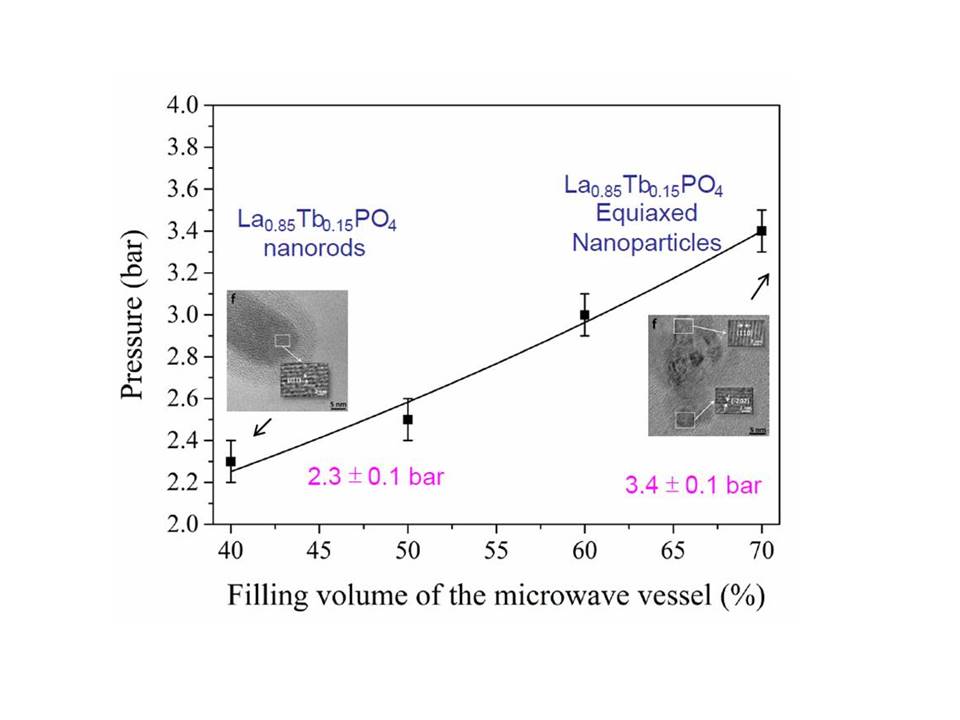
Lanthanide cations such as Eu3+ and Tb3+ offer outstanding optical, magnetic, and bio-affinity properties, and not surprisingly are being widely used for example as up conversion materials, catalysts, and fluorescence labels for biological detection. If they are fabricated in the form of nanorods, nanowires or hollow spheres, their luminescent efficiency and display resolution are further enhanced as a result of both their marked shape-specific and quantum-confinement effects. Among various possible hosts for lanthanide dopants, LaPO4 is noteworthy due to the potential high light yields of the resulting doped materials. In order to design the above-mentioned morphologies specific chemical synthesis methods have been developed and are considered in this study.